| Home | Sources Directory | News Releases | Calendar | Articles | | Contact | |
Slavery in Britain and Ireland
| The neutrality of this article is disputed. Please see the discussion on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until the dispute is resolved. (September 2009) |

| Part of a series on |
| Slavery |
|---|
| Early history |
| History – Antiquity – Aztec Ancient Greece – Rome Medieval Europe Thrall – Kholop – Serfdom |
| Slavery and religion |
| The Bible – Judaism Christianity – Islam |
| By country or region |
| Africa – Atlantic – Arab Coastwise – Angola Barbary Coast Britain and Ireland British Virgin Islands Brazil – Canada – India – China Iran – Japan – Libya – Mauritania Ottoman empire Romania – Spanish New World Sudan – Sweden – Texas – United States |
| Contemporary |
| Modern Africa – Debt bondage Peonage – Penal labour Sexual slavery – Wage slavery Unfree labour – Human trafficking Contemporary slavery |
| Opposition and resistance |
| Timeline – Abolitionism Compensated emancipation Opponents of slavery–Ž Slave rebellion – Slave narrative |
Slavery in Britain and Ireland dated from before Roman occupation. Chattel slavery virtually disappeared after the Norman Conquest. It was finally abolished by the Slavery Abolition Act 1833 (which made some exceptions for other parts of the British Empire). The prohibition on slavery and servitude is now codified under Article 4 of the European Convention on Human Rights, incorporated into UK law by the Human Rights Act 1998.
Contents |
[edit] Before 1066
From before Roman times, the practice of slavery was normal in Britannia as it was an institution in the Roman Empire. Slaves were routinely exported.[1][2] Anglo-Saxons continued the slave system, sometimes in league with Norse traders and often selling slaves to the Irish.[3] In the early fifth century the Romano-Briton Saint Patrick was captured by Irish raiders and taken as a slave to Ireland. Early Irish law makes numerous reference to slaves and semi-free sencléithe. A female slave (cumal) was often used as a currency unit, e.g. in expressing the honour price of people of certain classes.[4]
Some of the earliest account of the Anglo-Saxon English comes from the account of the fair-haired boys from York seen in Rome by Pope Gregory the Great. In the seventh century the English slave Balthild rose to be queen of the Frankish king Clovis II. Legal penalties and economic pressures that led to default in payments maintained sources of supply. Under ecclesiastical pressure, however, As the feudal order congealed in England during the 12th century, villeinage took the place of outright slavery;Anglo-Saxon opinion turned against the sale of English abroad: a law of Ine of Wessex stated that anyone selling his own countryman, whether bond or free, across the sea, was to pay his own wergild in penalty, even when the man so sold was guilty of crime.[5] Nevertheless, in the 11th century there was still a slave trade operating out of Bristol, as a passage in the Vita Wulfstani makes clear.[6]
[edit] Norman Englands
According to the Domesday Book census in 1086, 10% of England's population was enslaved.[7][8] In 1102 the Council of Westminster convened by Anslem issued a decree: "Let no one hereafter presume to engage in that nefarious trade in which hitherto in England men were usually sold like brute animals."[9] However, the Council had no legislative powers, and no act of law was valid unless signed by the monarch. As the feudal order congealed during the 12th century, the reduced status of the villein rendered outright slavery largely obsolete; the last form of this enforced servitude had disappeared in Britain by the beginning of the 17th century.
[edit] Transportation
Transportation to the colonies as an indentured servant served as punishment for both major and petty crimes in England and Ireland from the 17th century until well into the 19th century. A sentence could be for life or a specific period. The penal system required the convicts to work, on government projects such as road construction, building works and mining, or be assigned to free individuals as unpaid labour. Women were expected to work as domestic servants and farm labourers. Similar to slaves, indentured servants could be bought and sold, could not marry without the permission of their owner, were subject to physical punishment, and saw their obligation to labor enforced by the courts.
A convict who had served part of his time might apply for a "ticket of leave" permitting some prescribed freedoms. This enabled some convicts to resume a more normal life, to marry and raise a family, and a few to develop the colonies while removing them from the society. Exile was an essential component and thought to be a major deterrent to crime. Transportation was also seen as a humane and productive alternative to execution, which would most likely have been the sentence for many if transportation had not been introduced.
The transportation of British citizens overseas can be traced back to the English Vagabonds act of 1597. During the reign of Henry VIII, it has been estimated that approximately 72,000 people were put to death for a variety of crimes.[10] An alternate practice, borrowed from the Spanish, was to commute the death sentence and allow the use of convicts as a labour force for the colonies. One of the first references to a person being transported comes in 1607 when ''an apprentice dyer was sent to Virginia' from Bridewell for running away with his master's goods.'' [11]. The act was little used despite attempts by James I who, with limited success, tried to encourage its adoption by passing a series of Privy Council Orders in 1615, 1619 and 1620[12].
Transportation wasn't often used as a criminal sentence until the Piracy Act 1717, (An Act for the further preventing Robbery, Burglary, and other Felonies, and for the more effectual Transportation of Felons, and unlawful Exporters of Wool; and for declaring the Law upon some Points relating to Pirates.) established a seven-year penal transportation as a possible punishment for those convicted of lesser felonies, or as a possible sentence that capital punishment might be commuted to by royal pardon. Transportation of criminals to North America was undertaken from 1718-1776. When the American revolution made it unfeasible to carry out transportation to the thirteen colonies, those sentenced to it were typically punished with imprisonment or hard labour instead. From 1787-1868, criminals convicted and sentenced under the act were transported to the colonies in Australia.
Following the Irish uprising in 1641 and subsequent Cromwellian invasion, the English Parliament passed the Act for the Settlement of Ireland in 1652 which classified the Irish population into one of several categories according to their degree of involvement in the uprising and subsequent war. Those who had participated in the uprising or assisted the rebels in any way were sentenced to be hanged and to have their property confiscated. Other categories of the Irish population were sentenced to banishment with whole or partial confiscation of their estates. Whilst the majority of the resettlement took place within Ireland to the province of Connaught, Dr William Petty, the Cromwells Army Physician-General, estimated that as many as 100,000 Irish men, women and children were transported to the colonies in the West Indies and in North America as indentured servants.[13] During the early colonial period, The Scots and the English, along with other western European nations, dealt with their "Gypsy problem" by transporting them as slaves in large numbers to North America and the Caribbean. Cromwell shipped Romanichal Gypsies as slaves to the southern plantations and there is documentation of Gypsies being owned by former black slaves in Jamaica.[14]
Long before the Highland Clearances, some chiefs, such as Ewan Cameron of Lochiel, sold some of his clan into indenture in North America. His goal was to alleviate over-population and lack of food resources in his glens.
Numerous Highland Jacobite supporters, captured in the aftermath of Culloden and rigorous Government sweeps of the Highlands, were imprisoned on ships on the Thames River. Some were sentenced to transportation to the Carolinas as indentured servants.[15]
[edit] Workhouse slavery
From the 17th century to the 19th century, workhouses took in people whose poverty left them no other alternative. They were employed under forced labor conditions. Workhouses took in abandoned babies, usually presumed to be illegitimate. When they grew old enough, they were used as child labour. Charles Dickens's represented such issues in his fiction. A life example was Henry Morton Stanley. This was a time when many children worked; if families were poor, everyone worked. Only in 1833 and 1844 were the first general protective laws against child labour, the Factory Acts, passed in Britain.[16]
[edit] Barbary pirates
On 20 June 1631, in an event known as the Sack of Baltimore, the village of Baltimore in County Cork, Ireland was attacked by Algerian pirates from the North African Barbary Coast. The pirates killed two villagers and captured almost the whole population of over 100 people, who were put in irons and taken to a life of slavery in North Africa.
Villagers along the south coast of England petitioned the king to protect them from abduction by Barbary pirates. Item 20 of The Grand Remonstrance,[17] a list of grievances against Charles I and presented to him in 1641, contains the following complaint about Barbary pirates of the Ottoman Empire abducting English people into slavery:
- "20. And although all this was taken upon pretense of guarding the seas, yet a new unheard-of tax of ship-money was devised, and upon the same pretense, by both which there was charged upon the subject near –700,000 some years, and yet the merchants have been left so naked to the violence of the Turkish pirates, that many great ships of value and thousands of His Majesty's subjects have been taken by them, and do still remain in miserable slavery."
[edit] African slaves
The first Englishman recorded to have taken slaves from Africa was John Lok, a London trader who, in 1555, brought to England five slaves from Guinea. A second London trader taking slaves at that time was William Towerson.
Admiral Sir John Hawkins of Plymouth, a notable Elizabethan seafarer, is widely acknowledged to be "the Pioneer of the English Slave Trade". In 1554'1555, Hawkins formed a slave trading syndicate of wealthy merchants. He sailed with three ships for the Caribbean via Sierra Leone, hijacked a Portuguese slave ship and sold the 300 slaves from it in Santo Domingo. During a second voyage in 1564 his crew captured 400 Africans and sold them at Rio de la Hacha, thus making a 60% profit for his financiers. A third voyage involved both buying slaves directly in Africa and capturing a Portuguese ship with its cargo; upon reaching the Caribbean, Hawkins sold all the slaves. On his return, he published a book entitled An Alliance to Raid for Slaves.
The number of African slaves brought to the British Isles was far less than the numbers that were sent to Britain's colonies. Most were household servants.[18]
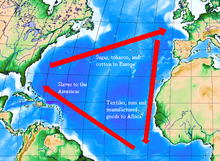
[edit] Triangular trade
By the 18th century, the slave trade became a major economic mainstay for such cities as Bristol and Liverpool, engaged in the so-called "Triangular trade". The ships set out from England, loaded with trade goods which were exchanged on the West African shores for slaves captured by local rulers from deeper inland; the slaves were transported through the infamous "middle passage" across the Atlantic, and were sold at considerable profit for labor in plantations. The ships were loaded with export crops and commodities, the products of slave labour, such as sugar and rum, and returned to England to sell the items.
[edit] Judicial decisions
John Locke, the philosophical champion of the Glorious Revolution argued against slavery (Ch.IV) and asserted that "every man has property in his own person" (–27, Ch.V). By the 18th century African slaves began to be brought into London and Edinburgh as personal servants.[citation needed] In a number of judicial decisions between slave merchants, it was tacitly accepted that slavery of Africans was legal.[citation needed] In Butts v. Peny (1677) 2 Lev 201, 3 Keb 785, an action was brought to recover possession of 100 slaves. The court held that slavery was legal in England in relation to infidels and that an action for trover would lie.[19]
But agitation saw a series of judgments repulse the tide of slavery. In Smith v. Gould (1705'07) 2 Salk 666, Holt CJ stated that by
"the common law no man can have a property in another."
But in 1729 the then-Attorney General and Solicitor General of England signed the Yorke-Talbot slavery opinion expressing their view (and, by implication, that of the Government) that slavery of Africans was lawful in England. At this time slaves were openly bought and sold on commodities markets at London and Liverpool. Slavery was also accepted in England's many colonies.
Lord Henley LC said in Shanley v. Harvey (1763) 2 Eden 126, 127 that as
"soon as a man sets foot on English ground he is free."
But it was not until R v. Knowles, ex parte Somersett (1772) 20 State Tr 1 the law was settled. A man called James Somersett was the slave of a Boston customs officer. They came to England, and Somersett escaped. Captain Knowles captured him and took him on his boat, Jamaica bound. Three abolitionists, saying they were his "godparents", applied for a writ of habeas corpus. One of Somerset's lawyers, Francis Hargrave, stated "In 1569, during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I, a lawsuit was brought against a man for beating another man he had bought as a slave overseas. The record states, 'That in the 11th [year] of Elizabeth [1569], one Cartwright brought a slave from Russia and would scourge him; for which he was questioned; and it was resolved, that England was too pure an air for a slave to breathe in'." He argued that the court had ruled in Cartwright's case that English Common Law made no provision for slavery, and without a basis for its legality, slavery would otherwise be unlawful as false imprisonment and/or assault.[20] In his judgment of 22 June 1772, Lord Chief Justice William Murray, Lord Mansfield, of the Court of King's Bench, started by talking about the capture and forcible detention of Somersett. He finished with:
"So high an act of dominion must be recognized by the law of the country where it is used. The power of a master over his slave has been exceedingly different, in different countries. The state of slavery is of such a nature, that it is incapable of being introduced on any reasons, moral or political, but only by positive law, which preserves its force long after the reasons, occasion, and time itself from whence it was created, is erased from memory. It is so odious, that nothing can be suffered to support it, but positive law. Whatever inconveniences, therefore, may follow from the decision, I cannot say this case is allowed or approved by the law of England; and therefore the black must be discharged."[21]
Several different reports of Mansfield's decision appeared. Most disagree as to what was said. The decision was only given orally; no formal written record of it was issued by the court. Abolitionists widely circulated the view that it was declared that the condition of slavery did not exist under English law, although Mansfield later said that all that he decided was that a slave could not be forcibly removed from England against his will.[22]
[edit] Abolition
The Church of England was implicated in slavery. Slaves were owned by the Anglican Church's Society for the Propagation of the Gospel in Foreign Parts (SPGFP), which had sugar plantations in the West Indies. When slaves were emancipated by Act of the British Parliament in 1834, the British government paid compensation to slave owners. Among those they paid were the Bishop of Exeter and three business colleagues, who received compensation for 665 slaves.[23]
William Wilberforce's Slave Trade Act 1807 abolished the slave trade in the British Empire. It was not until the Slavery Abolition Act 1833 that the institution finally was abolished.
[edit] Modern evaluation
Historians and economists have debated the economic effects of slavery for Great Britain and the North American colonies. Most analysts agree it allowed the formation of capital that financed the Industrial Revolution. Profits of the slave trade and of West Indian plantations amounted to less than 5% of the British economy at the time of the Industrial Revolution, so while it was economically important, it was not key to industrialization. Slave labour was integral to early settlement of the colonies, which had too few people. Also, slave labour produced the major consumer goods that were the basis of world trade during the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries: coffee, cotton, rum, sugar, and tobacco. Slavery was far more important to the profitability of plantations and the economy in the American South; and the slave trade and associated businesses were important to New York and New England both.[24]
In 2006, the then British Prime Minister, Tony Blair, expressed his deep sorrow over the slave trade, which he described as "profoundly shameful".[25] Some campaigners still demand reparations from the former slave trading nations.[26]
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ Strabo, Geographica book 4 chapter 5: Britain, Ireland, and Thule. http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Strabo/4E*.html "It bears grain, cattle, gold, silver, and iron. These things, accordingly, are exported from the island, as also hides, and slaves, and dogs"
- ^ Museum of Wales. Artefacts from Llyn Cerrig Bach. Gang Chain (Slave Chain) http://www.museumwales.ac.uk/en/2369/
- ^ Slave Trading in Anglo-Saxon and Viking England
- ^ International Journal of Historical Archaeology| Volume 8, Number 2 / June, 2004 | Lest the Lowliest Be Forgotten: Locating the Impoverished in Early Medieval Ireland
- ^ H. R. Loyn, Anglo-Saxon England and the Norman Conquest, 2nd ed. 1991:90.
- ^ Noted by Loyn 1991:90 note 39.
- ^ Domesday Book Slave
- ^ House of Commons Hansard Debates for 20 Mar 2007
- ^ Loyn 1991:90.
- ^ 1911 Encyclopedia Britannica, Capital punishment
- ^ Beier, A.L. (1985) Masterless Men: The Vagrancy Problem in England, 1560 -1640, London: Methuen, p. 163
- ^ Balak, Benjamin, and Jonathan M. Lave. 2002. 'The Dismal Science of Punish- ment: The Legal-Economy of Convict Transportation to the American Colonies'
- ^ "The curse of Cromwell", A Short History of Ireland, BBC Northern Ireland
- ^ http://www.tshaonline.org/handbook/online/articles/RR/pxrfh.html
- ^ (John Prebble: Culloden 1963)
- ^ "The Life of the Industrial Worker in 19th-Century Britain"
- ^ "The Grand Remonstrance, with the Petition accompanying it", Constitution Society, URL last accessed 6 December 2006.
- ^ [1]
- ^ See also Gelly v. Cleve (1694) 1 Ld Raym 147; later applying different reasoning Chamberlain v. Harvey (1697) 1 Ld Raym 146 and Smith v Gould (1705-07) 2 Salk 666
- ^ Matter of Cartwright, 11 Elizabeth; 2 Rushworth's Coll 468 (1569)
- ^ Somerset v Stewart Lofft 1-18; 11 Harg. State Trials 339; 20 Howell's State Trials 1, 79-82; 98 Eng Rep 499-510 (King's Bench, 22 June 1772) from Howell's text, http://medicolegal.tripod.com/somersetvstewart.htm#p51-rhc
- ^ See generally, S.M.Wise, Though the Heavens May Fall, Pimlico (2005)
- ^ Church apologises for slave trade
- ^ "Was slavery the engine of economic growth?", Digital History, University of Houston
- ^ Blair 'sorrow' over slave trade
- ^ Africa Reparations Movement (UK)
|
SOURCES.COM is an online portal and directory for journalists, news media, researchers and anyone seeking experts, spokespersons, and reliable information resources. Use SOURCES.COM to find experts, media contacts, news releases, background information, scientists, officials, speakers, newsmakers, spokespeople, talk show guests, story ideas, research studies, databases, universities, associations and NGOs, businesses, government spokespeople. Indexing and search applications by Ulli Diemer and Chris DeFreitas.
For information about being included in SOURCES as a expert or spokesperson see the FAQ or use the online membership form. Check here for information about becoming an affiliate. For partnerships, content and applications, and domain name opportunities contact us.